
That is Bare Capitalism fundraising week. 216 donors have already invested in our efforts to fight corruption and predatory conduct, significantly within the monetary realm. Please be a part of us and take part by way of our donation web page, which reveals the way to give by way of verify, bank card, debit card, PayPal. Clover, or Sensible. Examine why we’re doing this fundraiser, what we’ve achieved within the final yr,, and our present objective, supporting the commentariat.
Yves right here. Reviews on the China successfully squeezing the uncommon earths market and the shortage of sturdy alternate options oddly skip over the way in which the US ceded its place within the uncommon earths market, with the US decline important many years in the past. From a 2010 publish:
Reader James S. highlighted a helpful article on the MIT Know-how Evaluate, “Can the U.S. Uncommon-Earth Trade Rebound?” Our solely quibble to this strong piece is its abstract, which underplays some essential elements of the article:
The U.S. has loads of the metals which can be essential to many green-energy applied sciences, however engineering and R&D experience have moved abroad.
In actual fact, the whereas the article does focus on US versus overseas engineering experience in uncommon earths mining, it describes in some element how tough uncommon earths mining is normally (extra precisely, not the discovering the supplies half, however separating them out) and the appreciable extra hurdles posed by doing it in a non-environmentally harmful method. Thus the rub isn’t merely buying sure bits of technological know-how, but additionally breaking additional floor in lowering environmental prices.
And this difficulty has steadily been talked about in passing in accounts of why uncommon earth manufacturing moved to China within the first place. It’s nasty, and superior economies weren’t eager to do the job. China was keen to take the environmental injury. As an example, the New York Occasions factors out:
China feels entitled to name the pictures due to a brutally easy environmental reckoning: It presently controls a lot of the globe’s uncommon earths provide not simply due to geologic success, though there may be a few of that, however as a result of the nation has been keen to do soiled, poisonous and sometimes radioactive work that the remainder of the world has lengthy shunned.
From the MIT Know-how Evaluate:
Getting from rocks to the pure metals and alloys required for manufacturing requires a number of steps that U.S. firms not have the infrastructure or the mental property to carry out….
Within the Nineteen Seventies and Eighties, the Mountain Go mine in California produced over 70 p.c of the world’s provide. But in 2009, none have been produced in the USA, and it will likely be tough, expensive, and time-consuming to ramp up once more…
The 2 mines that shall be stepping up manufacturing soonest are Mountain Go, being developed by Molycorp, and the Mount Weld mine, which is being developed by Lynas, exterior Perth, Australia. Mountain Go has the sting of already having been established. However the firm can’t use the processes used within the mine’s heyday: they’re each economically and environmentally unsustainable.
A number of elements make purification of uncommon earths sophisticated. First, the 17 components all are likely to happen collectively in the identical mineral deposits, and since they’ve related properties, it’s tough to separate them from each other. In addition they are likely to happen in deposits with radioactive components, significantly thorium and uranium. These components can turn into a menace if the “tailings,” the slushy waste product of step one in separating uncommon earths from the rocks they’re present in, will not be handled correctly…
Mountain Go went into decline within the Nineteen Nineties when Chinese language producers started to undercut the mine on value similtaneously it had questions of safety with tailings. When the Mountain Go mine was working at full capability, it produced 850 gallons of waste saltwater containing these radioactive components each hour, day by day of the yr. The tailings have been transported down an eleven-mile pipeline to evaporation ponds. In 1998, Mountain Go, which was then owned by a subsidiary of oil firm Unocal, had an issue with tailing leaks when the pipeline burst; 4 years later, the corporate’s allow for storing the tailings lapsed.
In the meantime, all through the Nineteen Nineties, Chinese language mines exploited their foothold within the rare-earth market. The Chinese language started unearthing the weather as a byproduct of an iron-ore mine known as Bayan Obo within the northern a part of the nation; getting each merchandise from the identical web site helped maintain costs low initially. And the nation invested in R&D round rare-earth aspect processing, finally opening a number of smaller mines, after which encouraging producers that use these metals to arrange services within the nation.
Again to the present publish. A second difficulty is the US negligence in both offering for or in any other case funding and supporting sources of provide in vassals loyal allies, given the significance of uncommon earths to protection manufacturing. However given how the shortcoming of the US and its NATO allies to fulfill Russian navy manufacturing and the way the output hole is widening in favor of Russia, once more reveals how our putative leaders can’t plan their manner out of a paper bag.
By Jennifer Kary for MetalMiner, the most important metals-related media web site within the US in line with third occasion rating websites. Initially revealed at OilPrice
- China’s restrictions on uncommon earth mining and exports have disrupted international provide chains and pushed up costs.
- US companies, significantly within the protection sector, are weak to those disruptions on account of their reliance on Chinese language uncommon earths.
- Diversifying provide chains, investing in home manufacturing and recycling, and exploring various applied sciences are essential methods for mitigating dangers.
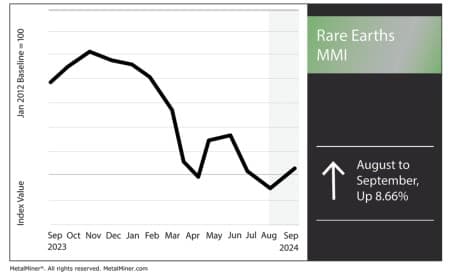
The Uncommon Earths MMI (Month-to-month Metals Index) managed to reverse and pull up by 8.66% after experiencing regular declines since Could. Quite a few elements of the uncommon earths index reversed value motion, together with neodymium and terbium oxide. China’s current crackdown on uncommon earth provides has prompted a shift within the international market, creating important bullish sentiment within the quick time period, the tendencies of which lined weekly in MetalMiner’s publication.
China’s Crackdown on Uncommon Earths Inflicting Worth Will increase
Over the previous few months, China’s crackdown on uncommon earth minerals and its broader regulatory tightening have despatched ripples by way of international markets. China has lengthy dominated the uncommon earths market, producing round 90% of the world’s refined uncommon earth output. This dominance permits Beijing to exert important affect over international provide chains for essential minerals like neodymium, praseodymium, and dysprosium, components important to the magnets utilized in all the pieces from electrical automobiles to wind generators.
Considered one of China’s predominant facilities for the manufacturing of uncommon earths, Jiangxi, is among the many provinces that spearheaded a four-month marketing campaign in opposition to unlawful mining actions. Whereas crackdowns on illicit mining profit the market in the long term, additionally they drive up uncommon earth costs within the quick time period.
The Provide-Demand Crunch
Many count on the demand for uncommon earths to maintain rising with the push for inexperienced vitality. In actual fact, some analysts predict a supply-demand mismatch on account of this continued international progress. China’s current actions to crack down on unlawful mining and tighten laws have positioned some contemporary pressure on the worldwide REE market.
Some analysts predict that the uncommon earth market will shift from a surplus to a world deficit by the tip of 2024. A smaller quantity additionally anticipate a possible international scarcity of 800 metric tons of NdPr, a essential element of everlasting magnets, by yr’s finish. In the meantime, China’s determination to scale back manufacturing quotas for uncommon earth components will probably widen this hole and push costs greater.
U.S. Protection Sector at Threat
China’s restrictions on exporting uncommon earth processing applied sciences have additionally prompted provide chain points for protection contractors, making it tougher to safe a dependable supply of supplies. Companies like Raytheon and Lockheed Martin want uncommon earth components for fighter jets, radars, and missile techniques. Conscious of this vulnerability, the U.S. Division of Protection has warned concerning the nationwide safety dangers tied to a heavy reliance on Chinese language uncommon earths.
What U.S. Companies Can Do to Mitigate Dangers
Whereas the reliance on Chinese language uncommon earths presents challenges, U.S. firms have choices to scale back their publicity and stop monetary losses.
For starters, U.S. firms should broaden the variety of their provider networks. Nations like Australia, Brazil, and Canada additionally maintain important uncommon earth reserves and proceed to ramp up manufacturing. Lately, firms like Australia’s Lynas Uncommon Earths have turn into key various suppliers, significantly for neodymium and praseodymium.
In the meantime, the U.S. authorities continues to actively encourage home manufacturing of uncommon earths to scale back dependency on Chinese language suppliers. MP Supplies, which operates the Mountain Go uncommon earth mine in California, performs a key function on this effort. The U.S. Division of Protection has additionally invested in constructing native uncommon earth processing vegetationto make sure the nation can supply these assets domestically.
One other technique entails recycling uncommon earth components from merchandise which have reached the tip of their life cycle. Though uncommon earth recycling expertise remains to be in its early levels, it holds important potential as a long-term answer to provide chain challenges. Corporations in industries like tech and automotive, which deal with massive volumes of uncommon earth-containing merchandise, can profit from investing in recycling infrastructure to recuperate these precious supplies from outdated electronics and autos.
