

Regardless of the prevailing security web, employee displacement continues to have extreme penalties that encourage the consideration of recent social insurance coverage packages. Wage insurance coverage is a novel coverage that briefly supplies extra revenue to employees who lose their job and develop into re-employed at a decrease wage. On this submit, we draw on proof from our current working paper analyzing the consequences of a U.S. wage insurance coverage program on employee earnings and employment outcomes. Amongst employees displaced by worldwide commerce, we discover that eligibility for wage insurance coverage elevated the chance of employment within the first two years following job loss and led to larger long-term earnings. This system resulted in web financial savings to the federal government as a result of employees collected fewer advantages and paid taxes on their elevated earnings. Collectively, these findings counsel that wage insurance coverage may help displaced employees extra successfully than conventional social insurance coverage packages.
A Novel Social Insurance coverage Program for Layoffs
Some jobs disappear. Industrial construction shifts attributable to technological change, worldwide competitors, offshoring, environmental rules, and different secular tendencies. Financial downturns typically result in extended unemployment, notably for employees in cyclical industries. Whatever the supply, the destructive results of displacement are extreme for a lot of employees, particularly those that have acquired job-specific abilities over lengthy tenures. Analysis suggests a causal hyperlink between job displacement and broader societal issues, together with decrease instructional attainment of kids, political polarization, and larger charges of mortality. Though unemployment insurance coverage briefly cushions the impacts of job loss, and retraining may help some employees achieve new abilities, these insurance policies are sometimes inadequate to compensate employees whose livelihoods are misplaced. Given the probability of ongoing labor market disruption from rising applied sciences, together with AI and decarbonization, policymakers could have an curiosity in different insurance policies.
One novel choice is wage insurance coverage, which supplies extra revenue to displaced employees who discover re-employment at a decrease wage. In current analysis, we studied the wage insurance coverage provisions of the U.S. Commerce Adjustment Help (TAA) program, which compensates employees who lose employment due to worldwide commerce. Displaced employees within the conventional TAA program take part in obligatory job coaching and obtain prolonged unemployment insurance coverage funds. Staff aged 50 or older are moreover eligible for a wage insurance coverage program, Reemployment Commerce Adjustment Help, which doesn’t require job coaching and as an alternative pays a wage subsidy of as much as half the distinction between employees’ pre- and post-separation wages for as much as two years. As a result of the quantity of the subsidy is proportional to the earnings decline, the coverage makes re-employment extra engaging, notably in lower-wage jobs, and directs bigger profit funds to employees who lose probably the most following displacement.
Estimating the causal impact of any voluntary social insurance coverage program is difficult. These receiving advantages could also be self-selected on numerous traits that relate to future outcomes. For instance, employees receiving wage insurance coverage funds should expertise wage declines to be eligible. Due to this fact, comparisons between those that obtain wage insurance coverage funds and people who don’t may mirror underlying variations within the two teams quite than the causal impact of the coverage on both personnel.
To bypass these challenges, we leverage the requirement that employees have to be age 50 or older when re-employed to be eligible for wage insurance coverage. After the TAA petition for a given layoff occasion is licensed by the Division of Labor, the related employees qualify for the baseline TAA advantages of coaching and prolonged UI funds described above. These aged 50 or older are eligible for each customary TAA advantages and wage insurance coverage, whereas youthful employees solely qualify for normal TAA. We due to this fact use a regression-discontinuity (RD) design that compares employment and earnings outcomes for employees who’re barely older than age 50 when displaced to these for employees who’re barely youthful. For instance, the chart under exhibits the connection between the proportion of displaced employees employed eight quarters following displacement and the employees’ age at separation. The seen bounce at age 50 displays the optimistic impact of wage insurance coverage on employees’ employment chance.
Employment Chance Jumps for These Eligible for Wage Insurance coverage
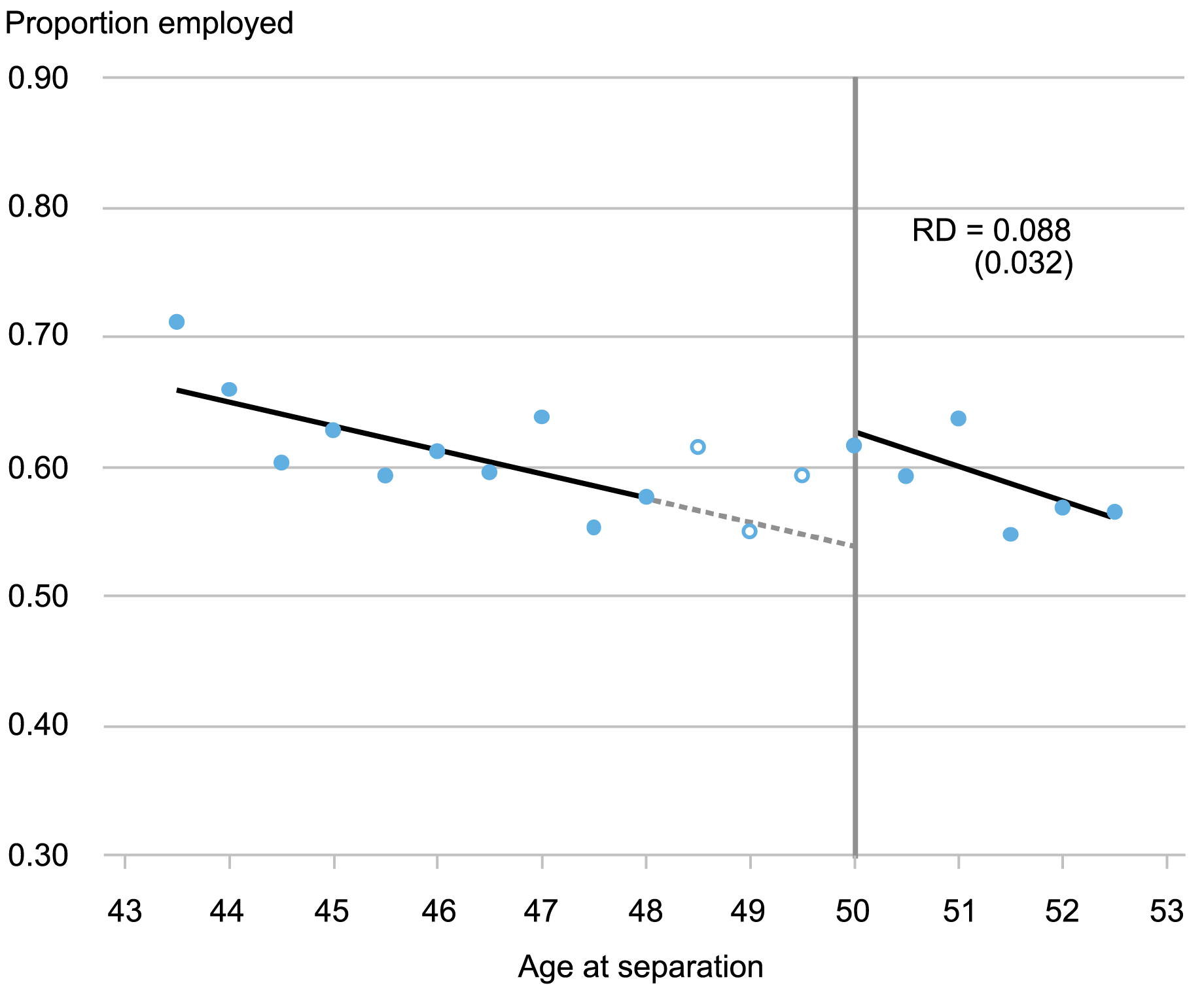
Sources: U.S. Division of Labor; U.S. Census Bureau; authors’ calculations.
Notes: The chart exhibits a regression discontinuity plot for the quarterly employment chance eight quarters following displacement. Hole dots signify omitted vary during which recipients are solely partially eligible for wage insurance coverage–see our paper for particulars. RD denotes regression discontinuity estimate of 8.8 proportion level larger proportion of employees employed, with customary error from the regression in parentheses.
To empirically estimate the impact of wage insurance coverage eligibility utilizing this method, we merge administrative knowledge on TAA petitions with the U.S. Census Bureau’s Longitudinal Employer-Family Dynamics knowledge set from 2007 to 2014, which allows us to trace employee earnings and employment outcomes for a number of years earlier than and after job loss. Our pattern covers 76,500 employees separating from roughly 1,000 TAA-petitioning companies. In comparison with the common displaced employee in the US, employees in our pattern are older, have longer tenure on the displacing agency, and have decrease instructional attainment—all traits that make the implications of job loss notably extreme. Certainly, the share of misplaced earnings “changed” after job loss (left-hand panel of the chart under) and the share of employees employed (right-hand panel) stay stunted for a number of years past preliminary layoffs in our pattern.
TAA-Eligible Staff Expertise Giant and Persistent Earnings and Employment Losses
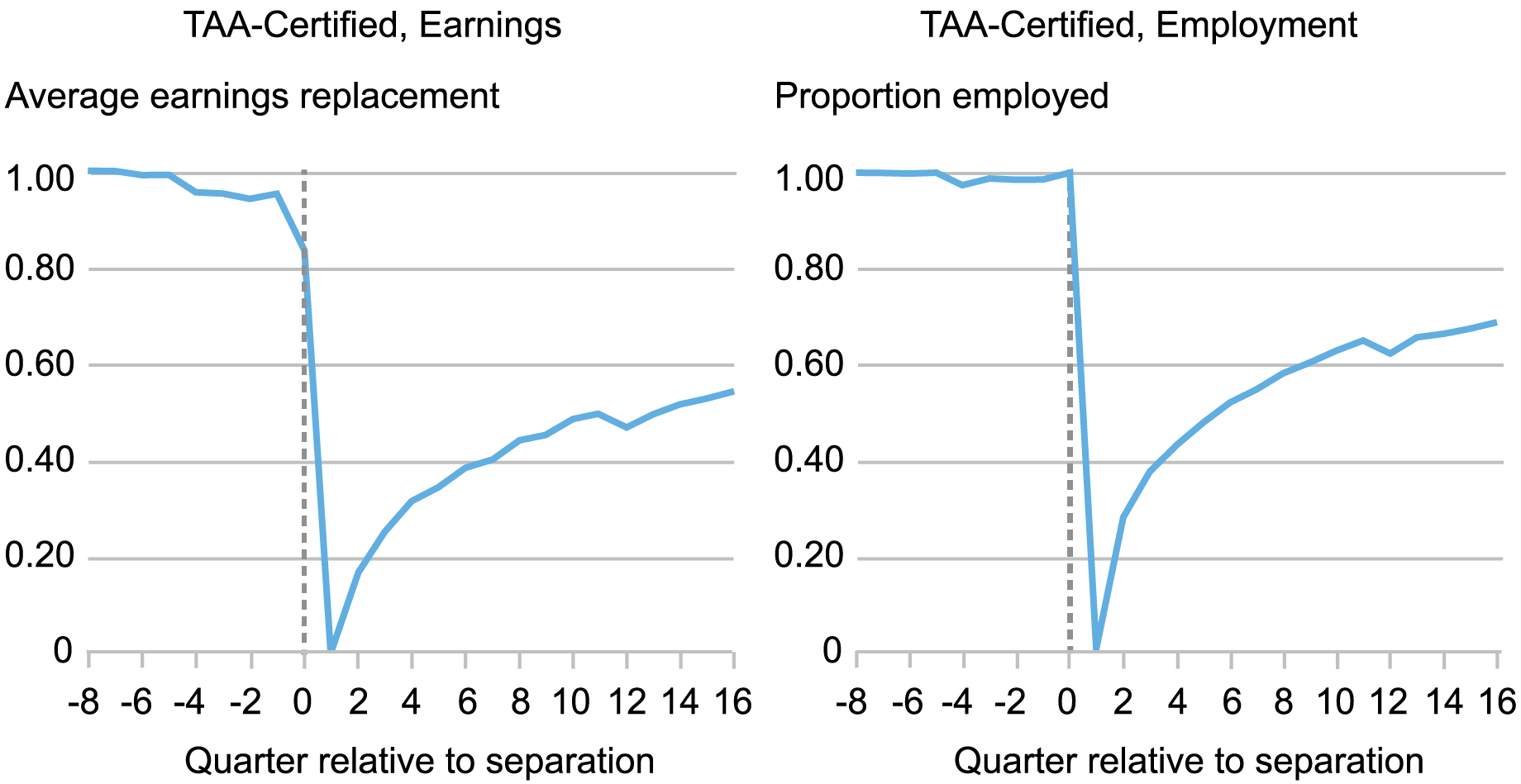
Sources: U.S. Division of Labor; U.S. Census Bureau; authors’ calculations.
Notes: The left-hand panel exhibits quarterly earnings over imply earnings from 5 to eight intervals previous to separation, during which employees are required to be employed to be within the pattern. The appropriate-hand panel exhibits the proportion of displaced employees (these employed in quarter 0 and non-employed in quarter 1) who’re employed in every quarter relative to separation.
The Affect of Wage Insurance coverage on U.S. Staff
We discover that wage insurance coverage eligibility boosted employees’ employment chances by 8 to 17 proportion factors within the two years after displacement earlier than fading to zero after 4 years (left-hand panel of chart under). Program eligibility additionally persistently elevated earnings (even omitting the worth of the subsidies). On common, wage insurance coverage eligibility elevated employees’ earnings by 10 % of their pre-displacement earnings, amounting to a rise of greater than $18,000, or 26 %, over the 4 years following a layoff (right-hand panel of chart under).
Results on Employment and Cumulative Earnings over Time
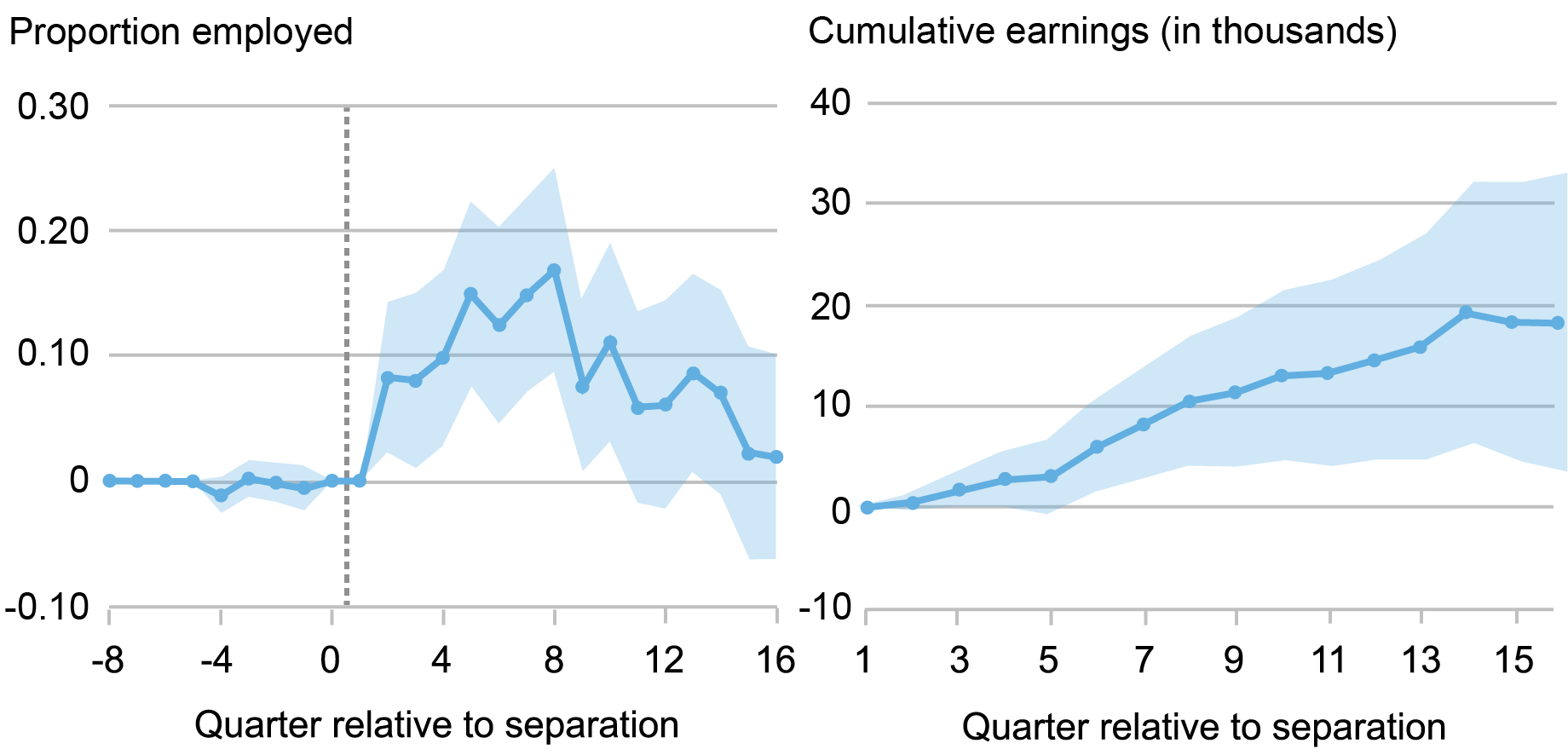
Sources: U.S. Division of Labor; U.S. Census Bureau; authors’ calculations.
Word: Every dot represents a separate regression coefficient in every quarter relative to separation utilizing our essential estimation technique, with 95 % confidence intervals denoted within the blue shaded areas.
Total, employees eligible for wage insurance coverage are inclined to return to work extra shortly following a displacing occasion. Shortening unemployment spells explains many of the optimistic results of wage insurance coverage eligibility on earnings, in keeping with prior proof that prolonged intervals of unemployment hurt employee outcomes. In distinction, the examine discovered minimal results on different employment outcomes, together with trade switching charges and employees’ variety of distinctive employers, geographic mobility, job high quality (measured by agency age, agency measurement, and earnings development charges), or the size of employment on the first job after displacement. The absence of declines in earnings or job high quality allays considerations that wage insurance coverage might need led to worse job matches and persistently decrease wages.
Wage insurance coverage is a really cost-effective coverage in our setting. In reality, we estimate that it pays for itself; the tax receipts on elevated earnings and decreased unemployment insurance coverage funds absolutely offset the prices of this system. Which means that this system led to web authorities financial savings whereas benefiting eligible employees. Against this, most different insurance coverage and coaching packages that focus on displaced employees are much less cost-effective.
A Promising Program Warranting Additional Examination
Though this explicit wage insurance coverage program is on the market solely to employees affected by commerce, the findings could have implications for a broader set of employees. Each upstream suppliers and downstream shoppers of companies dealing with commerce competitors are eligible for TAA, so this system’s attain extends past slim industries and geographic areas and contains the service sector.
Regardless of these compelling findings, vital questions on wage insurance coverage stay. For instance, it might be priceless to grasp how wage insurance coverage impacts different vital outcomes like mortality, which has been proven to extend after job loss. Additionally, a bigger scale wage insurance coverage program may lead employers to decrease wage affords, with the data that a few of their candidates will obtain subsidies. This response would blunt the favorable results for employees that we discover in a smaller-scale program. Nonetheless, the prevailing program was cost-effective, and our outcomes counsel that wage insurance coverage is a promising coverage to help economically weak employees.

Ben Hyman is a analysis economist in City and Regional Research within the Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York’s Analysis and Statistics Group.
Brian Kovak is a professor economics and public coverage at Carnegie Mellon College.
Adam Leive is an assistant professor of public coverage on the College of California, Berkeley.
Find out how to cite this submit:
Ben Hyman, Brian Kovak, and Adam Leive , “Wage Insurance coverage: A Potential Coverage for Displaced Staff,” Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York Liberty Road Economics, July 17, 2024, https://libertystreeteconomics.newyorkfed.org/2024/07/wage-insurance-a-potential-policy-for-displaced-workers/.
Disclaimer
The views expressed on this submit are these of the creator(s) and don’t essentially mirror the place of the Federal Reserve Financial institution of New York or the Federal Reserve System. Any errors or omissions are the duty of the creator(s).